By Gaaitzen de Vries
University of Groningen
The TWIN SEEDS report “GVC competitiveness regarding business functions” identifies Global Value Chains (GVCs) by tracing the flow of goods and services across countries as described in a world input-output table. This allows tracing the incomes that are directly and indirectly generated in the production of final manufacturing goods. The report subdivides the value added by the type of business function carried out, such as R&D, management, back-office, production, logistics and marketing. The value added of a particular function is proxied by the income of workers with occupations that relate to the activity. This way the distribution of value added across functions can be determined and specialisation patterns analysed.
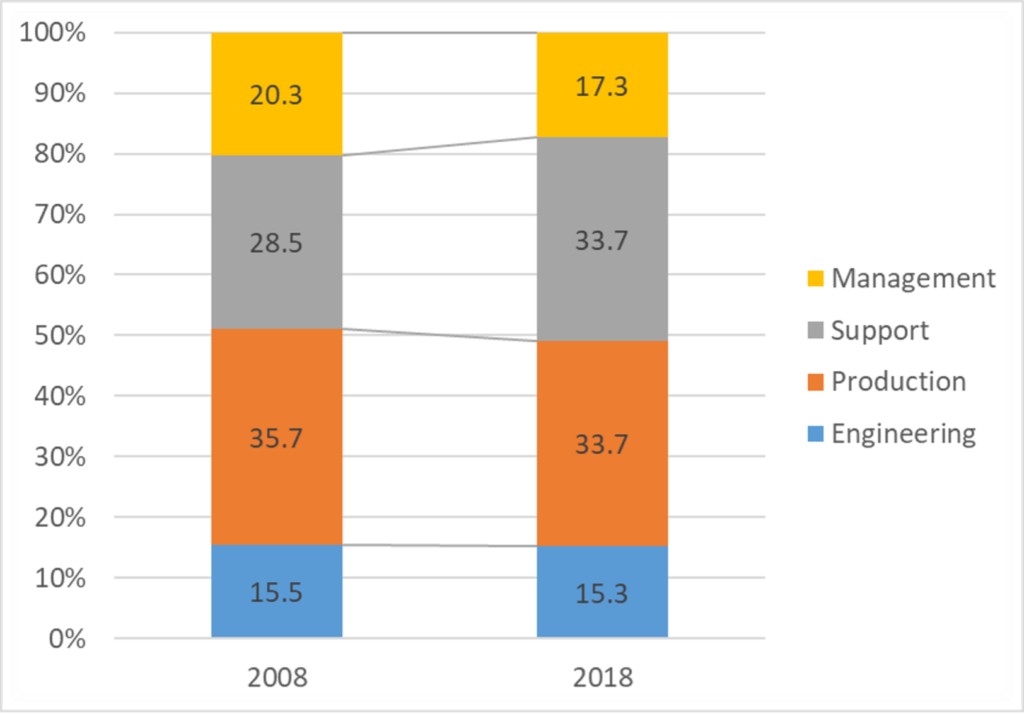
In this Figure, it is observed that about two thirds of EU income in manufactures’ GVCs comes from pre- and post-production activities. This increased during the period from 2008 to 2018. In particular, the share of support activities (such as marketing and after sales services) increased by 5.2 percentage points. In contrast, production activities declined by 2.0 percentage points. This suggests a clear but gradual specialisation pattern away from production activities and towards the upstream and downstream end of global value chains. Still almost one third of income in GVC is earned with production activities.
The report also traces the sectoral origins of changes in business functions for the EU. The GVC approach measures direct and indirectly embodied activities in final products. A substantial part of income shares across business functions originates from services sectors, in particular business services for pre- and post-production activities. The share of production activities declined, and the results suggest this partly originated from a decline in manufacturing industries, such as machinery and metal manufacturing. Much of the increase in pre- and post-production activities originates in industry.
About 2.5 (1.3) percentage points of the 5.2 (-0.1) percentage points change in support (engineering) activities originates in industry. Support activities also expanded in services, in particular in business services, rising by 1.4 percentage points. These business services are a heterogeneous grouping, consisting of architecture, research, consulting, and various other services. Some of these business services are closely related to pre- and post-production activities (e.g. R&D and design) and have expanded considerably during the past decades. Overall, it suggests the aggregate pattern of specialisation in pre- and post-production activities is broad based.
Notes: Manufactures GVC income directly and indirectly involved in the production of final manufacturing goods. Calculations based on the OECD Inter-Country Input-Output Tables, release November 2021, and the Occupation Database. Source: de Vries (2023) TwinSeeds report titled GVC competitiveness regarding business functions.
